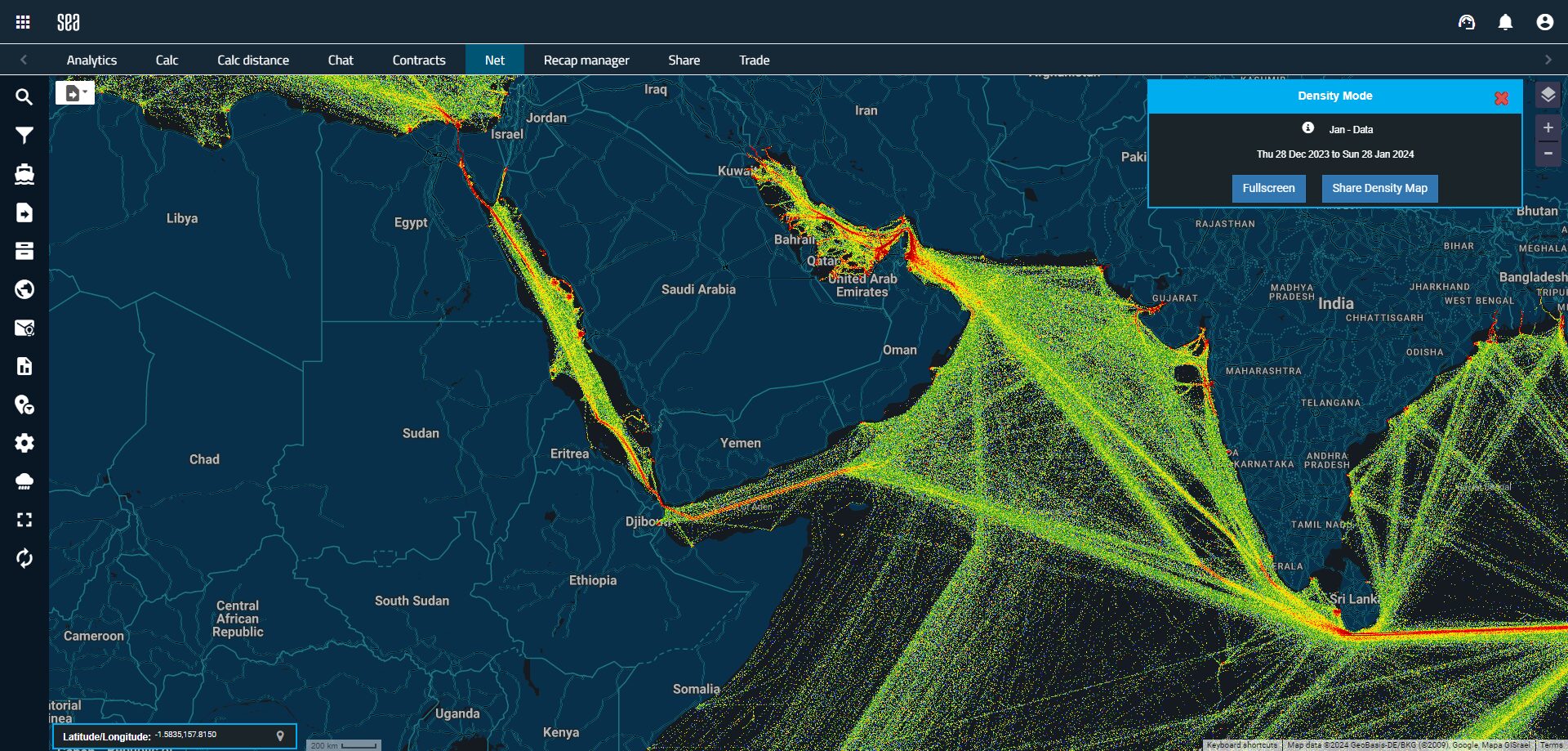
Ongoing tensions with the shipping crisis in the Red Sea have resulted in a notable decline in vessel traffic through the Suez Canal and Gulf of Aden – one of the busiest shipping routes in the world. As a response to the heightened threat in the Red Sea, an increasing number of vessels are chartering alternative courses, favouring the Cape of Good Hope. Leveraging Sea’s Pre-Trade Intelligence and Analytics solution, we have observed a strategic shift among vessels, with altered routes and accelerated steaming speeds aimed at minimising potential delays.
Red Sea shipping crisis – route diversions and increased steaming speeds
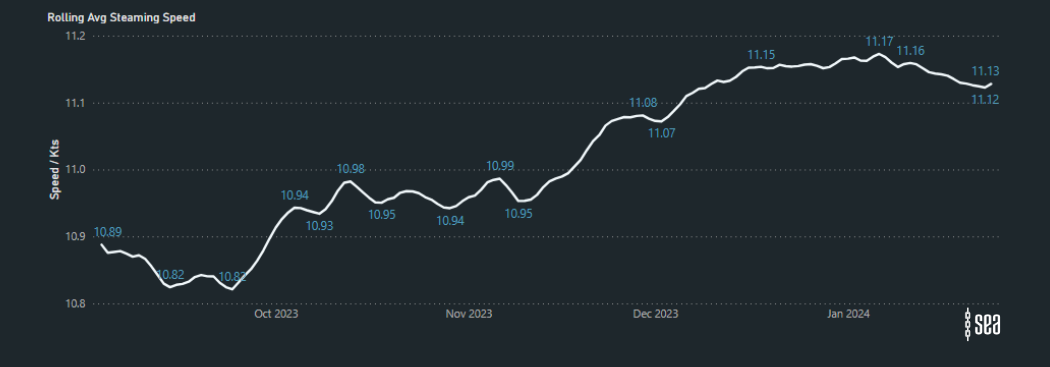
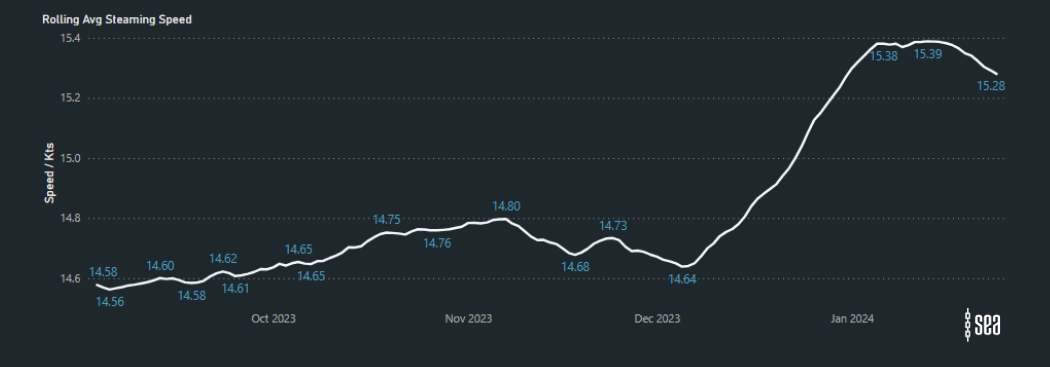
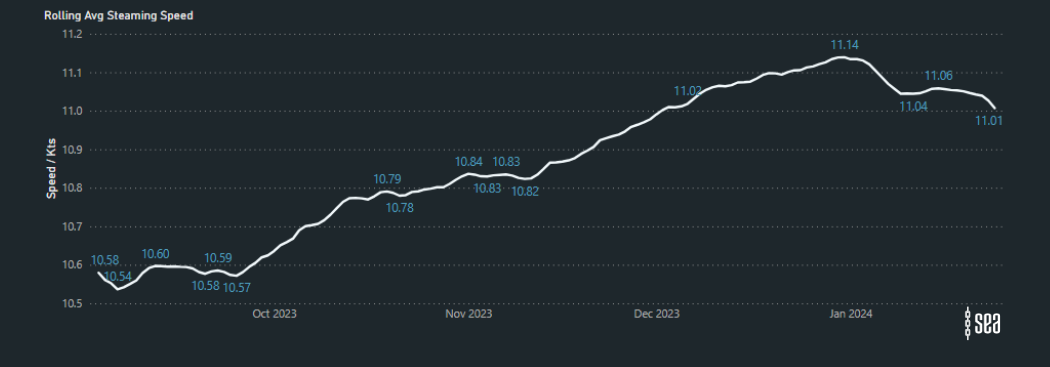
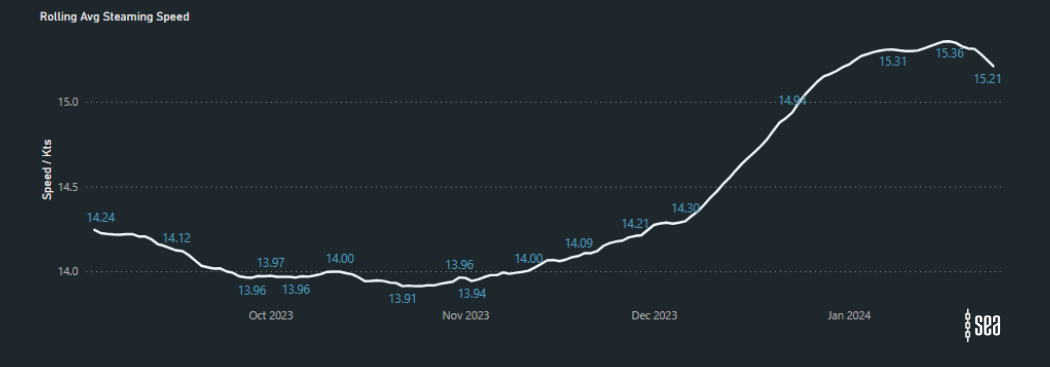
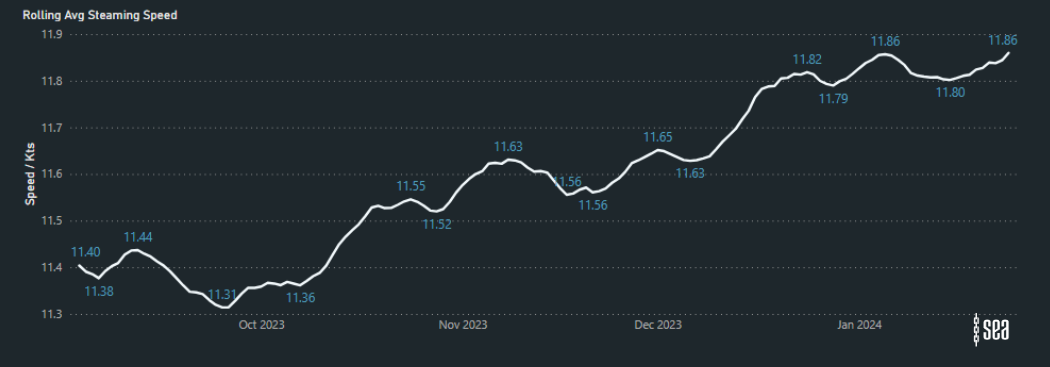
The latest analysis on the Sea platform reveals a trend in rerouting of vessels to avoid the Suez Canal, particularly evident in Post Panamax Containerships along the West Coast of Africa. Between October 2023 and January 2024, there has been a remarkable 27% surge in the average steaming speeds of these vessels.
Average Steaming Speeds West Coast Africa (COGH to Tangier):
Average Steaming Speeds on the East Coast of Africa (Bab al Mandab Strait to COGH):
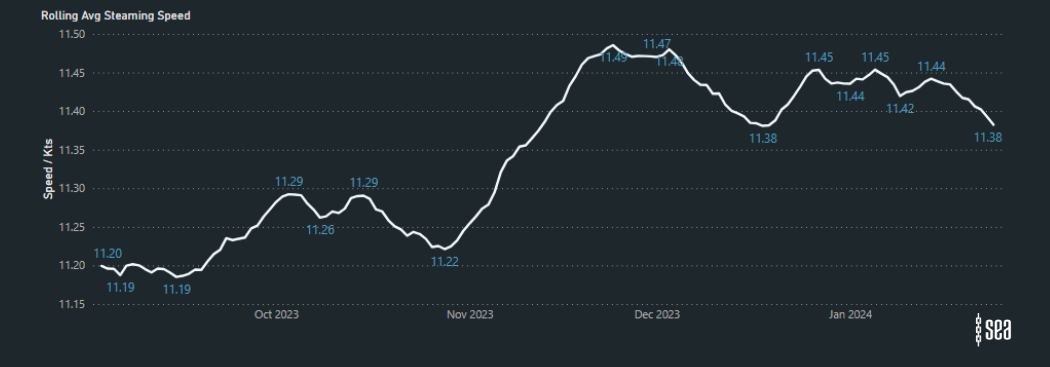
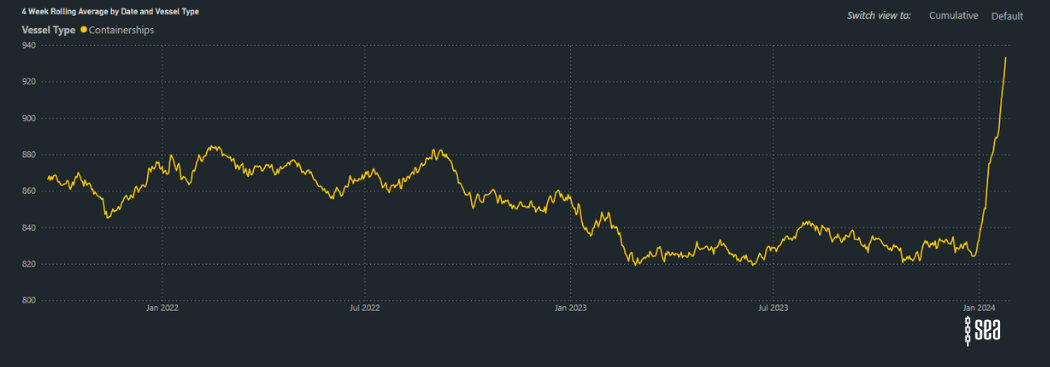
The graph below illustrates a notable increase in the average distance of containership voyages, showcasing in real-time the industry’s response to the impact of the Suez.
Global environmental impact
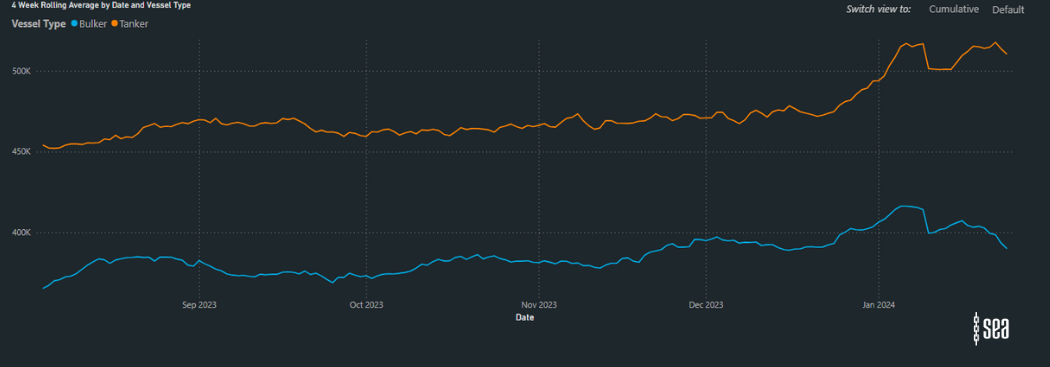
Importantly, these trends are beginning to predict a global increase in emissions across container, bulker and tanker categories. Specifically, a 17% rise in emissions for tankers and a 13% increase for bulkers, when compared to October 2023, is anticipated. This surge is attributed to the extended tonne miles resulting from diversions and the elevated average speeds of fleets navigating these altered routes.
The availability of vessels
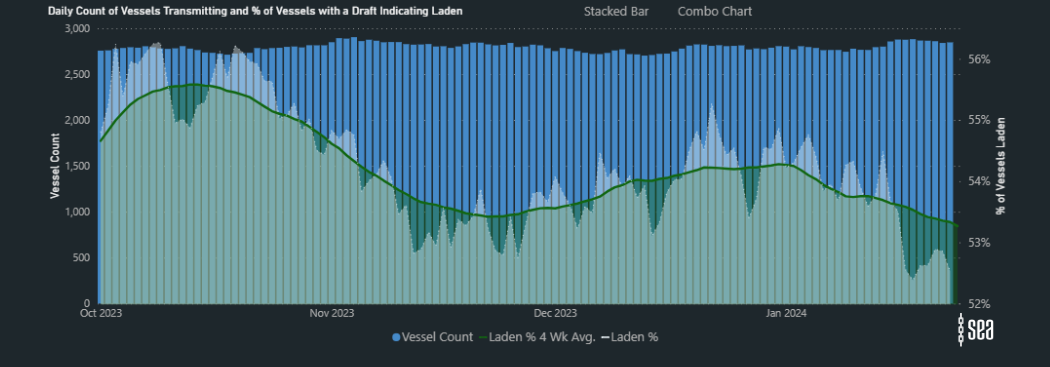
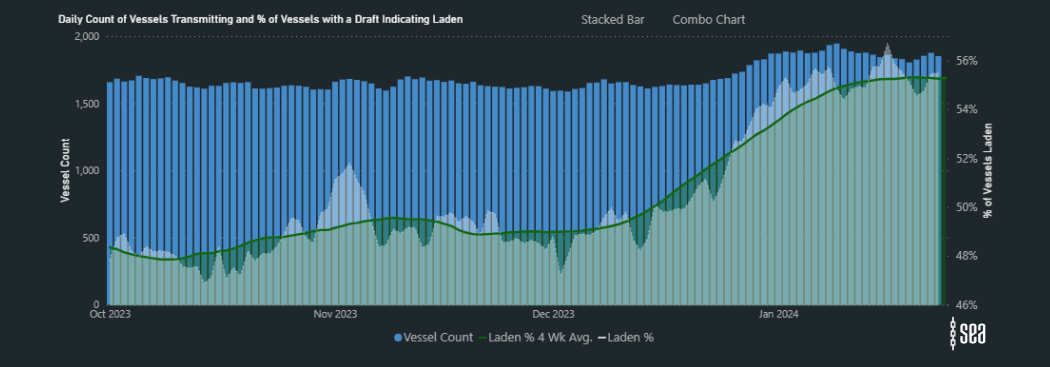
Notably, there has been a fluctuation in vessel supply, with a marked drop in the percentage of laden vessels across the East Coast of Africa and Indian Ocean. In contrast, there has been a noteworthy 17% increase in vessels laden on the West Coast of Africa.
As the shipping industry navigates geopolitical challenges, it is crucial to understand the multifaceted repercussions of altered shipping routes. With these evolving dynamics, it is more important now than ever before to have informed decision-making in an ever-changing maritime landscape.
Get in touch with us using the button below to learn more and get access to the Pre-Trade Intelligence and Analytics solution.
Share this article
Don’t miss the latest news and insights - subscribe to our newsletter
For press enquiries, please email news@sea.live